Here is a list of some of the most well-known and studied cannabinoids, including some of their properties and potential effects:
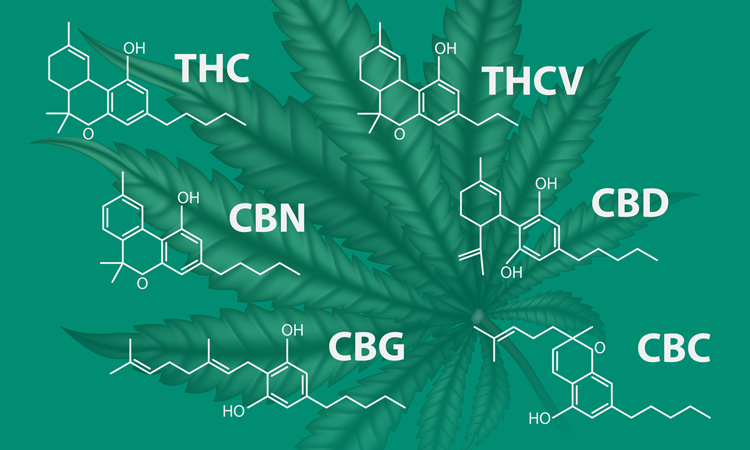
- Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) – psychoactive, pain relief, anti-inflammatory, appetite stimulant
- Cannabidiol (CBD) – non-psychoactive, pain relief, anti-inflammatory, anxiety relief, neuroprotective
- Cannabinol (CBN) – mildly psychoactive, sedative, anti-inflammatory, antibiotic, appetite stimulant
- Cannabigerol (CBG) – non-psychoactive, pain relief, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, anti-tumor
- Cannabichromene (CBC) – non-psychoactive, pain relief, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, anti-tumor, neuroprotective
- Tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV) – psychoactive, appetite suppressant, anti-inflammatory, anti-convulsant
- Cannabidivarin (CBDV) – non-psychoactive, anti-convulsant, anti-inflammatory, potential treatment for autism spectrum disorders
- Delta-8-tetrahydrocannabinol (Delta-8-THC) – mildly psychoactive, pain relief, appetite stimulant, anti-inflammatory
- Cannabidiolic acid (CBDA) – non-psychoactive, potential anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor effects, potential treatment for nausea and vomiting
- Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) – non-psychoactive, potential anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, and anti-tumor effects, potential treatment for nausea and vomiting
- Cannabigerolic acid (CBGA) – non-psychoactive, potential anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor effects, precursor to other cannabinoids
- Cannabichromenic acid (CBCA) – non-psychoactive, potential anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor effects, precursor to other cannabinoids.
Note that there are many other cannabinoids that have been identified and studied, and new ones are still being discovered. Additionally, the levels and composition of cannabinoids can vary depending on the specific strain of cannabis plant and how it is grown and processed.
Cannabinoids are a diverse group of chemical compounds found in the cannabis plant, which have been the subject of much scientific and medical research in recent years. These compounds interact with the endocannabinoid system in the body, which plays a key role in regulating a wide range of physiological and cognitive processes, including pain sensation, appetite, mood, and memory.
There are over 100 different cannabinoids that have been identified in cannabis, each with its own unique chemical structure and potential therapeutic properties. The two most well-known cannabinoids are tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD), which have different effects on the body.
THC is responsible for the psychoactive effects of cannabis, which can include feelings of euphoria, altered perceptions, and impaired cognitive function. It works by binding to cannabinoid receptors in the brain and nervous system, activating them and causing a range of effects.
CBD, on the other hand, does not produce a “high” and has been studied for its potential therapeutic benefits. It is believed to work by modulating the activity of the endocannabinoid system, rather than directly binding to cannabinoid receptors. CBD has been studied for its potential use in treating a wide range of medical conditions, including epilepsy, anxiety, pain, and inflammation, among others.
Other cannabinoids found in cannabis include cannabigerol (CBG), cannabinol (CBN), and tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV), each of which has its own unique chemical and biological properties. These compounds have also been studied for their potential medical uses, and ongoing research is exploring their potential therapeutic benefits.
In addition to the cannabinoids found in cannabis, there are also other compounds that may contribute to the plant’s therapeutic effects. These include terpenes, which are aromatic compounds found in many plants, and flavonoids, which are plant pigments that have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
While the use of cannabinoids for medical purposes is still a relatively new area of research, there is growing evidence to suggest that they may have a range of potential therapeutic benefits. However, there are also risks associated with their use, including the potential for side effects and interactions with other medications.
The regulatory environment surrounding the use of cannabinoids is also complex, with different countries and jurisdictions having different laws and regulations governing their use. It is important for individuals considering the use of cannabinoids for medical purposes to consult with a healthcare professional and to source products from reputable manufacturers to ensure quality and safety.
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in the use of cannabinoids for the treatment of epilepsy, particularly in children with severe forms of the condition that do not respond to conventional treatments. In clinical trials, CBD has been shown to be effective in reducing the frequency and severity of seizures in some patients with epilepsy.
Cannabinoids have also been studied for their potential use in the treatment of anxiety and mood disorders. Research has shown that CBD may have anxiolytic and antidepressant effects, and may be effective in reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression.
In addition, cannabinoids have been studied for their potential use in the treatment of pain and inflammation. Both THC and CBD have been shown to have analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties, and may be effective in reducing pain and inflammation associated with a range of conditions, including arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and cancer.
There is also growing interest in the potential use of cannabinoids in the treatment of cancer. While research in this area is still in its early stages, studies have shown that cannabinoids may have anti-tumor effects and may be effective in killing or slowing the growth of cancer cells.
Despite the potential benefits of cannabinoids, there are also risks associated with their use. THC, in particular, can cause a range of side effects, including impaired cognitive function, hallucinations, and paranoia. CBD, while generally well-tolerated, can also cause side effects in some people, including fatigue, diarrhea, and changes in appetite and weight.
In addition, the long-term effects of using cannabinoids for medical purposes are not yet fully understood, and there may be risks associated with long-term use, particularly in children and adolescents.
The regulatory environment surrounding the use of cannabinoids for medical purposes is also complex, with different laws and regulations governing their use in different countries and jurisdictions. In some places, the use of cannabinoids for medical purposes is legal, while in others it is restricted or illegal.
In summary, cannabinoids are a diverse group of chemical compounds found in the cannabis plant that have potential therapeutic benefits for a range of medical conditions. While research in this area is still ongoing, cannabinoids have been studied for their potential use in the treatment of epilepsy, anxiety and mood disorders, pain and inflammation, and cancer, among other conditions. However, there are also risks associated with their use, and the regulatory environment surrounding their use is complex. As such, it is important for individuals considering the use of cannabinoids for medical purposes to consult with a healthcare professional and to source products from reputable manufacturers.
The use of cannabinoids for medical purposes is still a relatively new area of research, and ongoing studies are exploring their potential therapeutic benefits and risks. In addition, there is a need for more research to better understand the long-term effects of using cannabinoids for medical purposes, particularly in vulnerable populations such as children and adolescents.
One of the challenges associated with using cannabinoids for medical purposes is the lack of standardization and regulation in the production and distribution of cannabinoid-based products. This can lead to variability in the potency and purity of these products, as well as the potential for contamination with harmful substances.
To address these issues, some countries and jurisdictions have implemented regulations governing the production, distribution, and use of cannabinoid-based products for medical purposes. These regulations may include requirements for product testing and labeling, as well as restrictions on the types and amounts of cannabinoids that can be used in these products.
In addition, healthcare professionals may play an important role in guiding the use of cannabinoids for medical purposes. This may involve assessing patients for potential risks and benefits, providing guidance on dosing and administration, and monitoring patients for adverse effects and drug interactions.
Overall, while the use of cannabinoids for medical purposes shows promise in treating a range of conditions, there is a need for further research to better understand their potential benefits and risks. It is also important for individuals considering the use of cannabinoids for medical purposes to consult with a healthcare professional and to source products from reputable manufacturers. With ongoing research and regulatory oversight, cannabinoids may continue to play an important role in the treatment of various medical conditions in the future.